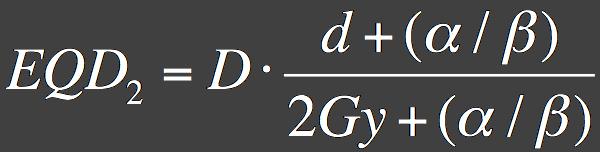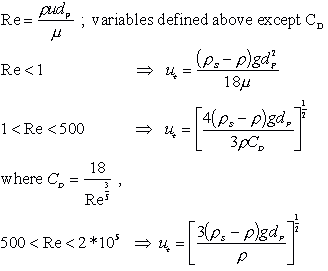Bed Calculation Formula

A gas strut calculator will take into account the direction of operation for the particular application the operating arm the weight and force relation.
Bed calculation formula. The doses are calculated as a guideline to allow conversion and comparability of different. Circular π r 2 x Depth Circular areas are also easy to calculate. Determine total bed days available by multiplying the total number of beds available in the hospital or inpatient unit by 365.
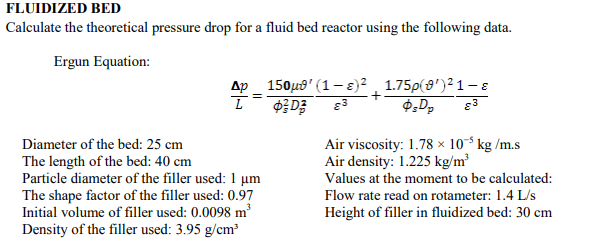
Catalyst weight top layer. θ θ cr 12 4 532. To better understand fluidization of a particle bed it is necessary to determine what range of flow rates allow fluidization and also what flow rates will begin to carry the particles out the top of the particle chamber.
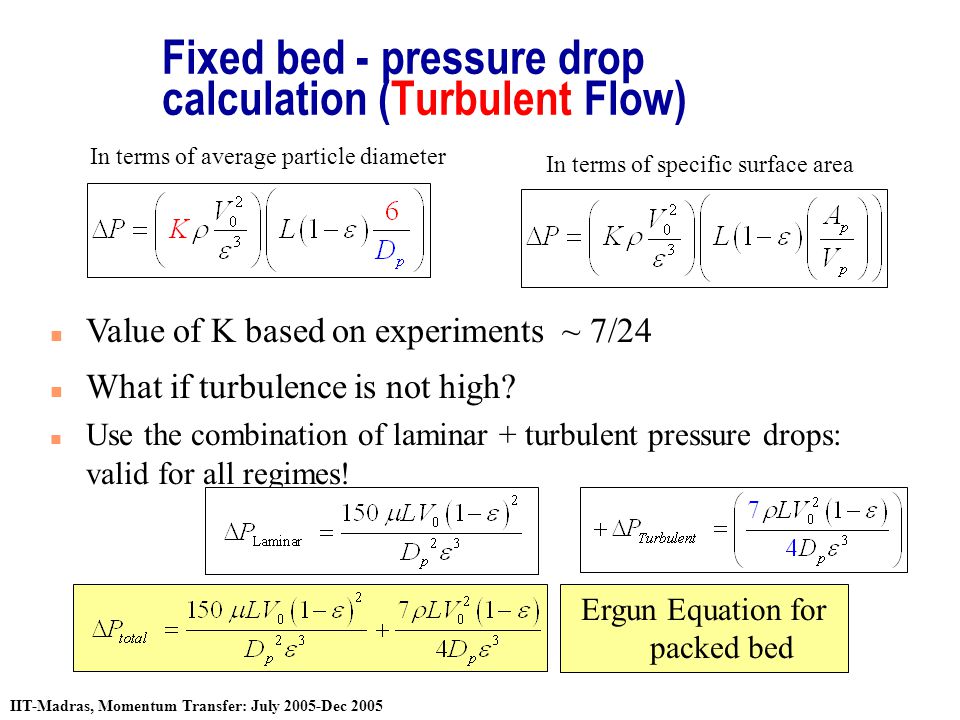
- Bed occupancy rate BOR. Bed volume L Bed height cm Column crossectional area cm2 1000. 1 650 kg 2 400 kg5 13 650 kg Wc 1 165013650 012.
To calculate CLR of 35 bend. Simply multiply 31415 π by the radius by the radius again by the depth or use our simple volume calculator. Occupancy rate Total number of bed-days during the year Number of beds available 365 days 100_.
1816 m3 550 kgm3 1 650 kg Catalyst weight layer 2 to 6. Use our gas strut force calculation formula below to work out the force needed. Then use this formula.
The biologically effective dose and equivalent dose in 2Gy calculators are based on the Linear Quadratic Model. Occupancy rate Total number of inpatient days for a given period x 100 Available beds x Number of days in the period. Note that this calculation does not take into consideration the extra volume in the conical end cells which are present in some columns for.