Bed Shear Stress
Within a certain range of stem spacing.
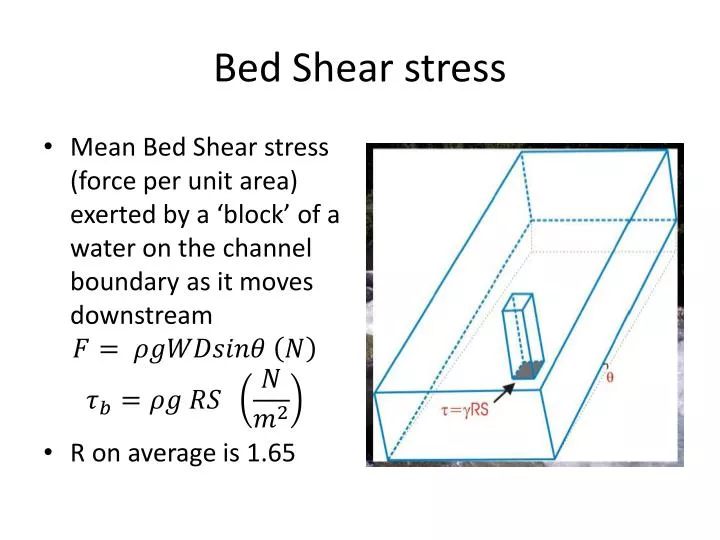
Bed shear stress. T Shear Stress Nm 2 g Weight Density of Water Nm 3 lbft. In bare-bed channels the bed shear stress can be estimated using several methods such as fitting the mean velocity profile based on a logarithmic Law of the Wall Figure 1a by the water surface slope method which relies on a momentum balance by extrapolating near-bed turbulent stress and using the empirical. Thompson et al 2004 the production of turbulence in stem wakes can enhance near-bed momentumtransferandincreasetherateofsedimententrainment Nezu and Onitsuka 2001.
Bed shear stress in open channel flows is often estimated from the logarithmic vertical velocity profile. To calculate Bed Shear Stress you need Specific weight of liquid y Bed Slope S and Diameter of Section D. Shear stress often denoted by τ is the component of stress coplanar with a material cross section.
Shear Stress t is a measure of the force of friction from a fluid acting on a body in the path of that fluid. The skin-friction bed shear-stress or bottom friction is the frictional force exerted on unit area of sea bed generated by currents andor waves. However most measuring devices used in the field do not allow for flow velocity to be measured very close to the bed.
Eg the weight of an earth-filled dam or dike may cause the subsoil to collapse like a small landslide. The Bed Shear Stress is defined as maximum value of shear stress at the bed point or bottom most point of the flowing stream in the channel is calculated using shear_stress Specific weight of liquid Bed Slope Diameter of Section. Wan Mechanics of Sediment Transport Translated into English ASCE Press Reston Virginia 1999.
The partitioning of shear between stems and the bed can reduce bed shear stress Lopez and Garcia 1998. Im writing a paper for presentation to the Stormwater Industry Association Queensland about shear stress and scour. Thus the maximum shear stress will occur either in the web of maximum shear flow or minimum thicknessAlso constructions in soil can fail due to shear.
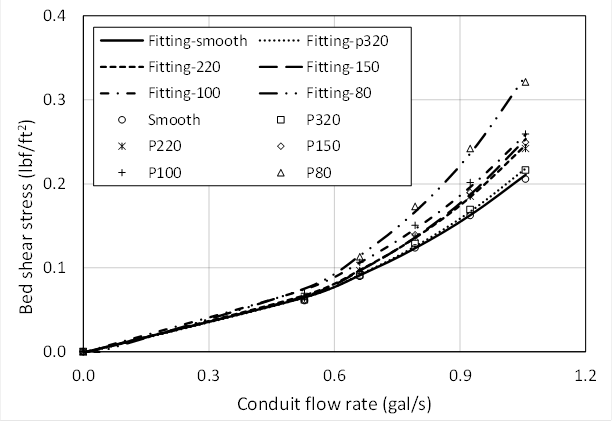
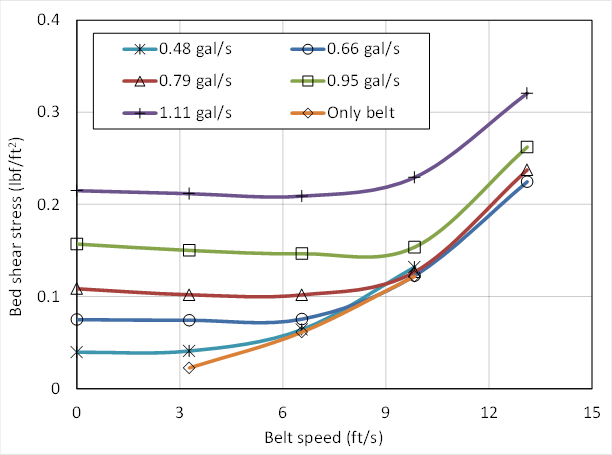
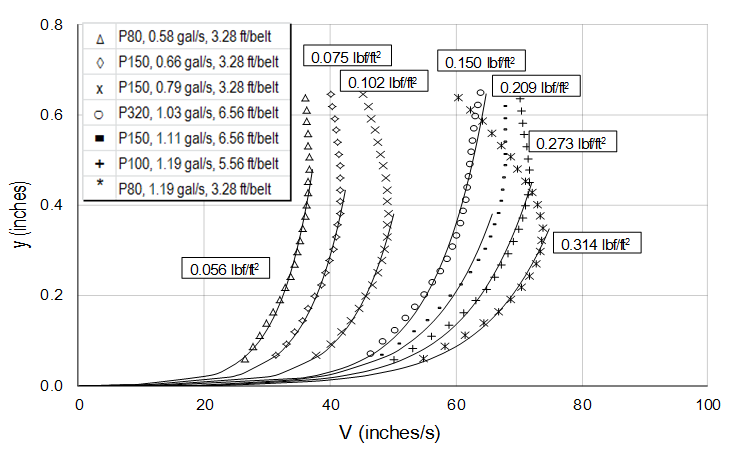
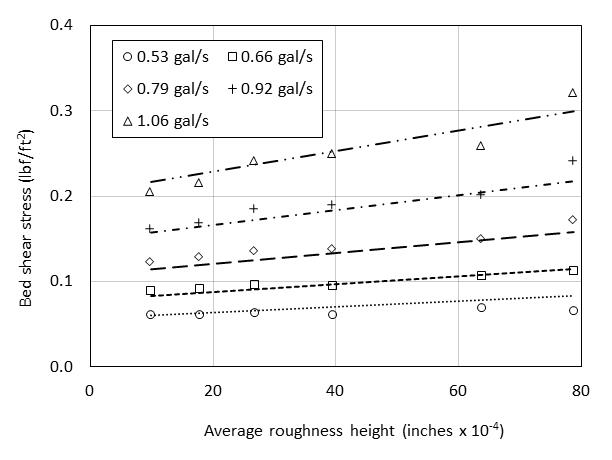
In relation to the bed shear stress values shown in Fig. The concept of bed shear stress is useful for understanding sediment transport. When stream flow lacks sufficient energy to move bedload non-competent discharges or where the bed is armoured or substratum particles are locked together imbricated the shear stress exerted on benthic biota by increased flows may be sufficient to alter the composition of benthic communities Lancaster.