Bedding Thickness Classification

Sidewall clearances are twelve 12 inches each side for sizes six 6 inches through twelve 12 inches.
Bedding thickness classification. The bedding is tamped thoroughly to ensure good compaction around and under the pipe. A quick help video to help you calculate the true thickness of a uniformly dipping bed using structure contours. 510 Screed-less bedding adhesive for laying marble floor.
Compacted ordinary fill 150 mm min. Bedding or lamination technically depending on stratum thickness but the important point is that the relatively thick bed typically comprises a very large number of much thinner internal laminae. Class A - Load Factor 22 - 34 In this method the bottom of the pipe is bedded in plain or reinforced concrete of suitable thickness.
100 achievable at 3 to 4mm bed depth. Suitable for most wallfloor tiles with lightly keyed backs. Class B bedding is the most commonly used bedding method.
Figure 3-3 is a chart that gives you all the official terminology. Soil classifications are presented in Chapter 3. Following is a discussion of some of these factors and the issues involved with incorporating them into the CMRR.
Classification cement-based adhesive is required. Choose From 22 Beautiful Colours. AASHTO Pavement Thickness Design Guide When designing pavement thickness for flexible and rigid pavements the following considerations should be used.
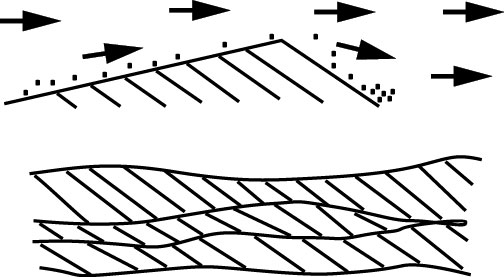
321 Stratification is officially subdivided into bedding and lamination de-pending upon the thickness of the strata and bedding and lamination are in turn subdivided according to thickness. 5 QUEENSLAND MA 2019 CONTENTS 10 Introduction 6 20 Siteworks 12 30 Footings slabs and set out 14 40 Masonry 18 50 Framing 25 60 Wall cladding 30. Bed Bed Finished surface Natural ground surface or compacted fill l c D6 or 150 mm whichever is greater l c D6 or 150 mm whichever is greater Refer ASNZS 3725 for cement stabilised soil Compacted D3 Compacted Compacted D3 Compacted Trench Embankment Compacted select fill 150 mm min.